
Remix & CDK fun
Published: 08-11-2022
Deploying Remix to AWS using the CDK.
I figured it was time to have a play with remix. As with all well designed products these days it's super quick to get going, however none of their 'starter' stacks scratched my AWS CDK deployment itch, so that's what the focus is here.
There is a an Architect starter stack, which deploys to AWS. I'm sure that's super handy and much easier for most, but I try to keep my IaC CDK-based. Having different tooling deploying to AWS in different ways gets confusing, and it's not that hard to do through the CDK. Under the hood, Architect is creating a SAM template and shipping that to AWS, so it shouldn't be too hard to figure out.
I'm not going to try and explain Remix because there are plenty of other, better resources for that! For CDK usage, what we need to know is that Remix is server-side rendered only. Code must run to make this happen.
The following diagram shows the architecture used to deploy Remix to AWS. CloudFront is helping serve content at the edge. Static files are fetched from S3 if not already cached. All other requests are served by a Lambda behind a API Gateway HTTP Proxy.
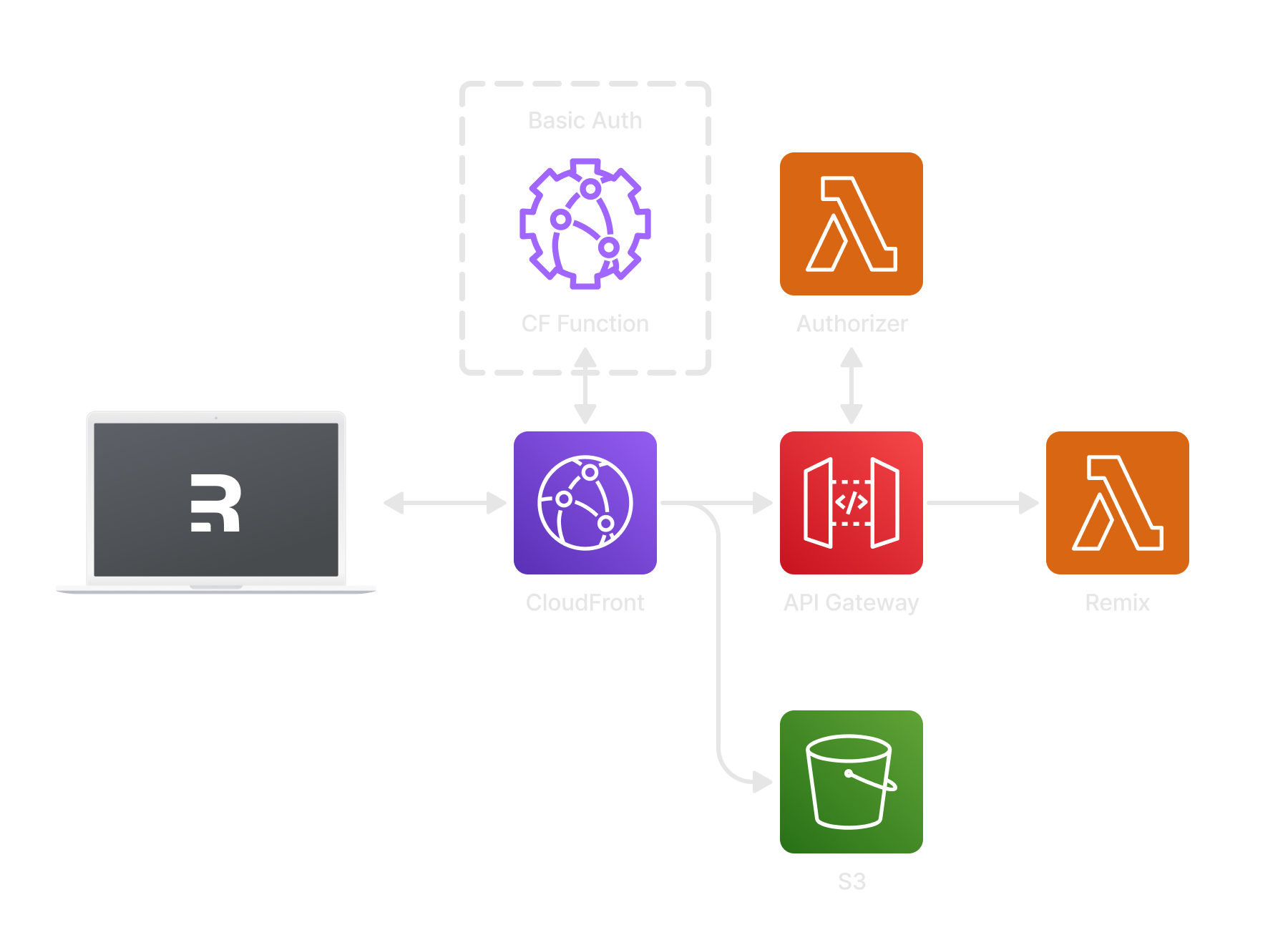
Why the authorizer?
We want to make sure that traffic is only served from CloudFront and not through the API Gateway endpoint. We do this to take advantage of the CDN HTTP caching for both static assets and dynamic pages (where applicable). The authorizer is used to check for a secret header written that will be added by CloudFront. There is also the added bonus of being able to use WAF in front of CloudFront if needed down-the-line (and not have it bypassed). WAF cannot be used directly with API Gateway V2 (HTTP Proxies) at the time of writing.
Why the CloudFront function?
We only want one live site at a time, so when deploying to other environments it would be nice to have them closed off from the big bad web and search crawlers. Basic auth is a simple way of achieving this and a CloudFront function is perfect for making that happen.
I'm not going to demonstrate how to bootstrap a basic TypeScript Remix app, it's over here. I started with a basic install rather than a starter stack.
Remix can't just be chucked into an API Gateway connected Lambda, it knows nothing about the event/context format that needs to be processed. Knowing that the Architect starter stack is also packaging Remix for APIG and Lambda, we can grab their handler and put it in a server.ts file:
import { createRequestHandler } from '@remix-run/architect';
import * as build from '@remix-run/dev/server-build';
export const handler = createRequestHandler({
build,
mode: process.env.NODE_ENV,
});
Next the config needs to be modified, so remix can be built for lambda as well as run in it's standard dev mode without the need for architect. This feels a little hacky but oh well...
/** @type {import('@remix-run/dev').AppConfig} */
module.exports =
process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? {
appDirectory: 'app',
cacheDirectory: './node_modules/.cache/remix',
assetsBuildDirectory: 'public/static/build',
publicPath: '/static/build/',
serverBuildTarget: 'arc',
server: './server.ts',
ignoredRouteFiles: ['**/.*', '**/*.css', '**/*.test.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}'],
}
: {
appDirectory: 'app',
publicPath: '/static/build/',
assetsBuildDirectory: 'public/static/build',
};
Importantly here, the server.ts file from above is being referenced as our server entry point. Compared to the default remix config, a static directory has been added to the assets path. This just makes it easier to create a CloudFront origin for serving static assets later on.
Adding a line to package.json created a production build command
"scripts": {
...
"build": "npm run build:css && remix build",
"build:prod": "export NODE_ENV=production; yarn build",
},
Building will create a server directory. server/index.js is the entry point for the Lambda function that get built a bit later.
Check out the full CDK stack code snippet at the end for all the code. Here are the stack props that will be used.
export interface RemixSiteProps extends StackProps {
existingHostedZoneDomain: string;
siteSubdomain: string;
basicAuth: string | undefined;
xOriginVerify: string;
certificateArnParameter: string | undefined;
certificateDomainParameter: string | undefined;
}
In the CDK code that follows, it is assumed that a hosted zone exists in the AWS account being used for deployment, and the domain name is passed in as a prop. Having control over the hosted zone is important for setting up subdomains and certificates.
Why is the subdomain and hosted zone domain being passed separately?
Flexibility and being unable to determine the hosted zone when multiple sub domains are stacked. The hosted zone domain is listed explicity here but could be grabbed from a SSM parameter, as it is created in advanced.
This example is pulled from a project where each environment (prod, dev etc.) has it's own AWS account and control over the environment domain (prod.mydomain.com, dev.mydomain.com etc.). This setup makes it easy to create certificate protected domains like remixsite.prod.mydomain.com, remixsite.dev.mydomain.com etc. in each account. The root domain can then be routed to the 'main' deployment separately.
certificateArn and certificateName?
When use of a pre-existing certificate is needed (because the account doesn't have authority over the domain for example), a pre-existing certificate arn and domain can specified through the certificateArnParameter and certificateDomainParameter props. These props point to SSM parameter store values. A more in-depth rambling about multi-account domain management will appear soon, but essentially this enables the root domain to be used from an account that doesn't own the root hosted zone (it requires some extra alias routing from root domain account as mentioned above).
export class RemixStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: RemixSiteProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
//---------------------------------
// Domain & Certificate
//---------------------------------
const zone = route53.HostedZone.fromLookup(this, 'Zone', {
domainName: props?.existingHostedZoneDomain!,
});
const siteDomain =
props?.siteSubdomain + '.' + props?.existingHostedZoneDomain;
let certificate;
let certificateDomain;
if (props?.certificateArnParameter && props?.certificateDomainParameter) {
const prodCertificateArn = ssm.StringParameter.valueForStringParameter(
this,
props?.certificateArnParameter
);
certificateDomain = ssm.StringParameter.valueForStringParameter(
this,
props?.certificateDomainParameter
);
certificate = acm.Certificate.fromCertificateArn(
this,
'importedProdCertificate',
prodCertificateArn
);
} else {
certificateDomain = siteDomain;
certificate = new acm.DnsValidatedCertificate(this, 'siteCertificate', {
domainName: siteDomain,
hostedZone: zone,
region: 'us-east-1', // Cloudfront only checks this region for certificates.
});
}
new CfnOutput(this, 'Certificate', { value: certificate.certificateArn });
}
}
certificate and certificateDomain will be referenced in the CloudFront distribution later.
The main remixLambda references the server/index.js file, created during the build process earlier as the entry point. NodejsFunction can be used to bundle TypeScript directly using ESBuild but here it's just grabbing the prebuilt files and creating a deployable asset.
To check the request is coming from CloudFront a small inline authorizer Lambda function is created. The x-origin-verify header is essentially a static password, and so can be cached for the maximum time allowed (1 hour).
The API Gateway is set up as a passthrough HTTP proxy.
export class RemixStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: RemixSiteProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
...
//---------------------------------
// Remix
//---------------------------------
const authLambda = new lambda.Function(this, 'authLambda', {
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_16_X,
handler: 'index.handler',
code: lambda.Code.fromInline(`
exports.handler = async function(event, ctx, cb) {
const authorization = event.headers.authorization || '';
if (event.headers['x-origin-verify'] === '${props?.xOriginVerify}') {
return { isAuthorized: true }
}
return { isAuthorized: false };
}
`),
logRetention: logs.RetentionDays.ONE_DAY,
});
authLambda.addPermission('apiGateway', {
principal: new iam.ServicePrincipal('apigateway.amazonaws.com'),
action: 'lambda:InvokeFunction',
});
new CfnOutput(this, 'authLambdaLogName', {
value: authLambda.logGroup.logGroupName,
});
const remixAuthorizer = new HttpLambdaAuthorizer(
'remixAuthorizer',
authLambda,
{
responseTypes: [HttpLambdaResponseType.SIMPLE],
identitySource:['$request.header.x-origin-verify'],
resultsCacheTtl: Duration.hours(1),
}
);
const remixLambda = new NodejsFunction(this, 'remixLambda', {
currentVersionOptions: {
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
},
entry: './server/index.js',
logRetention: RetentionDays.THREE_DAYS,
memorySize: 1024,
timeout: Duration.seconds(10),
});
const remixLmabdaIntegration =
new apigatewayv2Integrations.HttpLambdaIntegration(
'remixLambdaProxy',
remixLambda
);
const remixHttpApi = new apigatewayv2.HttpApi(this, `remixHttpApi`, {
defaultIntegration: remixLmabdaIntegration,
defaultAuthorizer: remixAuthorizer,
});
}
}
What about Lambda@Edge?
Lambda at the edge looks like a cool option in some scenarios. It does however have bundle size constraints, and if database calls to a central location are needed anyway, any performance gains could be muted. Using CloudFront in front of a centrally located API Gateway will reduce latency, by routing traffic over the AWS network (instead of the public internet). Note also, that API Gateways don't exist at the edge and so a different handler would be needed to call Lambda@edge directly from CloudFront.
CloudFront is the application entry point and needs to route requests to either API Gateway for dynamic pages or S3 for static assets - origins are used to accomplish this.
A CloudFront function is set to intercept requests and check for the correct basic auth headers. If they don't exist, the function returns an error which causes the browser to show a basic auth input dialog. The CloudFront function is small and so writing it inline seems appropriate. If no basic auth is required (root domain), no function is set and the x-origin-verify is set using a CloudFront header option.
export class RemixStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: RemixSiteProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
...
//---------------------------------
// S3
//---------------------------------
const staticBucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'staticBucket', {
publicReadAccess: false,
blockPublicAccess: s3.BlockPublicAccess.BLOCK_ALL,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, // NOT recommended for production code
autoDeleteObjects: true, // NOT recommended for production code
});
new S3Deployment.BucketDeployment(
this,
'staticBucketDeployment',
{
sources: [S3Deployment.Source.asset('./public')],
destinationBucket: staticBucket,
}
);
new CfnOutput(this, 'staticBucketArn', { value: staticBucket.bucketArn });
//---------------------------------
// CloudFront
//---------------------------------
const cachePolicy = new cloudfront.CachePolicy(this, `cachePolicy`, {
cookieBehavior: cloudfront.CacheCookieBehavior.all(),
defaultTtl: Duration.seconds(0),
minTtl: Duration.seconds(0),
maxTtl: Duration.days(10),
queryStringBehavior: cloudfront.CacheQueryStringBehavior.all(),
enableAcceptEncodingGzip: true,
enableAcceptEncodingBrotli: true,
headerBehavior: cloudfront.CacheHeaderBehavior.allowList(
'authorization',
'x-origin-verify'
),
});
let functionAssociations;
if (props?.basicAuth) {
const basicAuthCloudfrontFunction = new cloudfront.Function(
this,
'basicAuthCloudfrontFunction',
{
code: cloudfront.FunctionCode.fromInline(`
function handler(event) {
var authHeaders = event.request.headers.authorization;
if (authHeaders) {
var authorization = authHeaders.value || '';
if (${encodedBasicAuthCondition}) {
return event.request;
}
}
var response = {
statusCode: 401,
statusDescription: "Unauthorized",
headers: {
"www-authenticate": {
value: 'Basic realm="Enter credentials"',
},
},
};
return response;
}
`),
}
);
functionAssociations = [
{
eventType: cloudfront.FunctionEventType.VIEWER_REQUEST,
function: basicAuthCloudfrontFunction,
},
];
}
const remixDistribution = new cloudfront.Distribution(
this,
`remixDistribution`,
{
domainNames: [certificateDomain],
certificate,
defaultBehavior: {
allowedMethods: cloudfront.AllowedMethods.ALLOW_ALL,
cachePolicy,
origin: new origins.HttpOrigin(remixHttpApi?.url!.split('/')[2], {
customHeaders: { 'x-origin-verify': props?.xOriginVerify! },
}),
viewerProtocolPolicy:
cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.REDIRECT_TO_HTTPS,
functionAssociations: functionAssociations,
},
additionalBehaviors: {
[`/static/*`]: {
origin: new origins.S3Origin(staticBucket),
viewerProtocolPolicy:
cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.REDIRECT_TO_HTTPS,
functionAssociations: functionAssociations,
},
},
}
);
new route53.ARecord(this, 'SiteAliasRecord', {
recordName: siteDomain,
target: route53.RecordTarget.fromAlias(
new targets.CloudFrontTarget(remixDistribution)
),
zone,
});
}
}
Should x-origin-verify be hardcoded?
Not really, the recommended way is to use Secrets Manager to rotate the header value. Although that's best for production, it's doesn't matter much for development.
Consuming the stack is really going to depend on how AWS accounts are structured and the CI/CD processes in place. You could have separate prod, staging, dev accounts. if it's just a frontend, staging might be in the production account for more realistic deployment checks. The dev account might contain all pull request branches.
The thing to remember is if deploying in the same account, the stack name needs to be unique (dynamic) and no resources can have explicit resource name (✅). The following bin/deploy.ts file is only designed to deploy one stack per account as the stack name is hardcoded (keeping it simple).
import 'source-map-support/register';
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { RemixStack } from '../stacks/remix-stack';
const stdEnv: {
account: string;
region: string;
} = {
account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT || '',
region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION || '',
};
const app = new cdk.App();
const existingHostedZoneDomain = app.node.tryGetContext(
'existingHostedZoneDomain'
);
// const siteSubdomain = app.node.tryGetContext('siteSubdomain'); Could use for dynamic subdomain
const basicAuth = app.node.tryGetContext('basicAuth');
const xOriginVerify = app.node.tryGetContext('xOriginVerify');
const certificateArnParameter = app.node.tryGetContext(
'certificateArnParameter'
);
const certificateDomainParameter = app.node.tryGetContext(
'certificateDomainParameter'
);
new RemixStack(app, 'remixStack', {
env: stdEnv,
existingHostedZoneDomain,
siteSubdomain: 'remixsite',
basicAuth,
xOriginVerify,
certificateArnParameter,
certificateDomainParameter,
});
No hardcoded env variables?
Because the stack is used across different accounts, the account number and region must be provided to the stack dynamically. This done using the OIDC credentials provider shown next.
There are a fair few different ways to structure AWS accounts and CI/CD deployments. This is a simple, single file, deploying a single branch to a single account. The flexibility gained by potentially using dynamic account details and stack names should allow more complex setups though, just not in this rambling.
With Open ID Connect, AWS secrets don't need to be stored in GitHub secrets any more. An AWS role can be created which grants access for GitHub and a certain repo/branch/environment to request temporary access tokens. These tokens can be used to deploy the application. The documentation is pretty good.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::123456123456:oidc-provider/token.actions.githubusercontent.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": "<repo:repo-org/repo-repo:*>"
},
"ForAllValues:StringEquals": {
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:iss": "https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com",
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
To preserve the flexibility of deploying to different accounts while not hardcoding or sharing basic auth and origin headers between then, GitHub environments can be used. Environments enable secrets to be stored per 'environment'. For the workflow below, BASIC_AUTH and X_ORIGIN_VERIFY secrets need to be created for a dev environment.
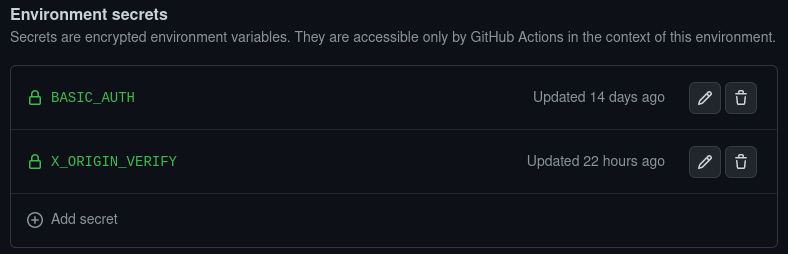
Below is the very simple deployment workflow for getting that CDK code into the wild. Note, the dev environment is being used to access the correct secrets.
name: deploy dev
on:
push:
branches: [dev]
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
environment: dev # Using the environment secrets
timeout-minutes: 15
# These permissions are needed to interact with GitHub's OIDC Token endpoint.
permissions:
id-token: write
contents: read
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: '3.x'
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: '16'
cache: 'yarn'
- name: yarn install
run: yarn install --immutable --immutable-cache --check-cache
# Add some tests?
- name: Configure AWS Credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
role-to-assume: <github-role-arn>
aws-region: eu-west-2
- name: Build frontend
run: |
yarn build:prod
- name: deploy to dev
run: |
yarn cdk deploy remixSiteDev --require-approval never -c basicAuth=${{ secrets.BASIC_AUTH }} -c xOriginVerify=${{ secrets.X_ORIGIN_VERIFY }} -c existingHostedZoneDomain='playground.serverlessup.com'
# More tests?
Note - Subdomain certificates take a while to create and delete. Adding a wildcard subdomain certificate per account can help. The wildcard could be used to serve all branch pull request deployments, as an example. Using a wildcard domain would require the certificate arn and domain be passed in, like suggested for the root domain solution.
It might look a bit complicated compared to a single Architect command, but understanding how AWS is serving the application while having direct access to make tweaks and properly support multi-account deployments is valuable.
Another low code way of hosting a frontend is Amplify (I used to do this). Amplify is good at building and serving static apps. It can even host SSR enabled NextJS (certain versions). The compromise you make is the build process is happening in Amplify, whether you like it or not, and framework support is also dependent on Amplify (although they are adding features to make supporting more SSR apps quicker I believe). Amplify is doing the same CloudFront - S3 - Lambda - Basic auth thingies under the hood. It wasn't really too hard to replicate while retaining full CI/CD control here though.
The services and architecture used to serve this remix app are applicable to most other frameworks. This site is built use NextJS and static generation, served from by CloudFront and S3. As well as handling basic auth, the CF function handles URL rewrites to make the routing work.
If later on down the line, there are some performance gains/cost savings to be had from using EC2, or a container service for hosting application processing, the CloudFront origin can be pointed there instead. APIG and Lambda do a pretty good job though!
import 'source-map-support/register';
import * as cdk from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { RemixStack } from '../stacks/remix-stack';
const stdEnv: {
account: string;
region: string;
} = {
account: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_ACCOUNT || '',
region: process.env.CDK_DEFAULT_REGION || '',
};
const app = new cdk.App();
const existingHostedZoneDomain = app.node.tryGetContext(
'existingHostedZoneDomain'
);
// const siteSubdomain = app.node.tryGetContext('siteSubdomain'); COuld use for dynamic subdomain
const basicAuth = app.node.tryGetContext('basicAuth');
const xOriginVerify = app.node.tryGetContext('xOriginVerify');
const certificateArnParameter = app.node.tryGetContext(
'certificateArnParameter'
);
const certificateDomainParameter = app.node.tryGetContext(
'certificateDomainParameter'
);
new RemixStack(app, 'remixStack', {
env: stdEnv,
existingHostedZoneDomain,
siteSubdomain: 'remixsite',
basicAuth,
xOriginVerify,
certificateArnParameter,
certificateDomainParameter,
});
import type { Construct } from 'constructs';
import { Duration, RemovalPolicy, Stack, CfnOutput } from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import type { StackProps } from 'aws-cdk-lib';
import { NodejsFunction } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda-nodejs';
import { RetentionDays } from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-logs';
import * as apigatewayv2 from '@aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2-alpha';
import * as apigatewayv2Integrations from '@aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2-integrations-alpha';
import * as cloudfront from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront';
import * as origins from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-cloudfront-origins';
import * as route53 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-route53';
import * as ssm from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-ssm';
import * as acm from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-certificatemanager';
import * as s3 from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3';
import * as S3Deployment from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-s3-deployment';
import * as targets from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-route53-targets';
import * as logs from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-logs';
import {
HttpLambdaAuthorizer,
HttpLambdaResponseType,
} from '@aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2-authorizers-alpha';
import * as lambda from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-lambda';
import * as iam from 'aws-cdk-lib/aws-iam';
export interface RemixSiteProps extends StackProps {
existingHostedZoneDomain: string;
siteSubdomain: string;
basicAuth: string | undefined;
xOriginVerify: string;
certificateArnParameter: string | undefined;
certificateDomainParameter: string | undefined;
}
export class RemixStack extends Stack {
constructor(scope: Construct, id: string, props?: RemixSiteProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
//---------------------------------
// Domain & Certificate
//---------------------------------
const zone = route53.HostedZone.fromLookup(this, 'Zone', {
domainName: props?.existingHostedZoneDomain!,
});
const siteDomain =
props?.siteSubdomain + '.' + props?.existingHostedZoneDomain;
let certificate;
let certificateDomain;
if (props?.certificateArnParameter && props?.certificateDomainParameter) {
const prodCertificateArn = ssm.StringParameter.valueForStringParameter(
this,
props?.certificateArnParameter
);
certificateDomain = ssm.StringParameter.valueForStringParameter(
this,
props?.certificateDomainParameter
);
certificate = acm.Certificate.fromCertificateArn(
this,
'importedProdCertificate',
prodCertificateArn
);
} else {
certificateDomain = siteDomain;
certificate = new acm.DnsValidatedCertificate(this, 'siteCertificate', {
domainName: siteDomain,
hostedZone: zone,
region: 'us-east-1', // Cloudfront only checks this region for certificates.
});
}
new CfnOutput(this, 'Certificate', { value: certificate.certificateArn });
//---------------------------------
// S3
//---------------------------------
const staticBucket = new s3.Bucket(this, 'staticBucket', {
publicReadAccess: false,
blockPublicAccess: s3.BlockPublicAccess.BLOCK_ALL,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY, // NOT recommended for production code
autoDeleteObjects: true, // NOT recommended for production code
});
new S3Deployment.BucketDeployment(this, 'staticBucketDeployment', {
sources: [S3Deployment.Source.asset('./public')],
destinationBucket: staticBucket,
});
new CfnOutput(this, 'staticBucketArn', { value: staticBucket.bucketArn });
//---------------------------------
// Remix
//---------------------------------
let encodedBasicAuthCondition;
if (props?.basicAuth) {
const encodedUserPass = Buffer.from(
`${props?.basicAuth}`,
'utf8'
).toString('base64');
encodedBasicAuthCondition = `authorization === 'Basic ${encodedUserPass}'`;
}
const authLambda = new lambda.Function(this, 'authLambda', {
runtime: lambda.Runtime.NODEJS_16_X,
handler: 'index.handler',
code: lambda.Code.fromInline(`
exports.handler = async function(event, ctx, cb) {
const authorization = event.headers.authorization || '';
if (event.headers['x-origin-verify'] === '${props?.xOriginVerify}') {
return { isAuthorized: true }
}
return { isAuthorized: false };
}
`),
logRetention: logs.RetentionDays.ONE_DAY,
});
authLambda.addPermission('apiGateway', {
principal: new iam.ServicePrincipal('apigateway.amazonaws.com'),
action: 'lambda:InvokeFunction',
});
new CfnOutput(this, 'authLambdaLogName', {
value: authLambda.logGroup.logGroupName,
});
const remixAuthorizer = new HttpLambdaAuthorizer(
'remixAuthorizer',
authLambda,
{
responseTypes: [HttpLambdaResponseType.SIMPLE],
identitySource: props?.basicAuth
? ['$request.header.authorization', '$request.header.x-origin-verify']
: ['$request.header.x-origin-verify'],
resultsCacheTtl: Duration.hours(1),
}
);
const remixLambda = new NodejsFunction(this, 'remixLambda', {
currentVersionOptions: {
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
},
entry: './server/index.js',
logRetention: RetentionDays.THREE_DAYS,
memorySize: 1024,
timeout: Duration.seconds(10),
});
const remixLmabdaIntegration =
new apigatewayv2Integrations.HttpLambdaIntegration(
'remixLambdaProxy',
remixLambda
);
const remixHttpApi = new apigatewayv2.HttpApi(this, `remixHttpApi`, {
defaultIntegration: remixLmabdaIntegration,
defaultAuthorizer: remixAuthorizer,
});
//---------------------------------
// CloudFront
//---------------------------------
const cachePolicy = new cloudfront.CachePolicy(this, `cachePolicy`, {
cookieBehavior: cloudfront.CacheCookieBehavior.all(),
defaultTtl: Duration.seconds(0),
minTtl: Duration.seconds(0),
maxTtl: Duration.days(10),
queryStringBehavior: cloudfront.CacheQueryStringBehavior.all(),
enableAcceptEncodingGzip: true,
enableAcceptEncodingBrotli: true,
headerBehavior: cloudfront.CacheHeaderBehavior.allowList(
'authorization',
'x-origin-verify'
),
});
let functionAssociations;
if (props?.basicAuth) {
const basicAuthCloudfrontFunction = new cloudfront.Function(
this,
'basicAuthCloudfrontFunction',
{
code: cloudfront.FunctionCode.fromInline(`
function handler(event) {
var authHeaders = event.request.headers.authorization;
if (authHeaders) {
var authorization = authHeaders.value || '';
if (${encodedBasicAuthCondition}) {
return event.request;
}
}
var response = {
statusCode: 401,
statusDescription: "Unauthorized",
headers: {
"www-authenticate": {
value: 'Basic realm="Enter credentials"',
},
},
};
return response;
}
`),
}
);
functionAssociations = [
{
eventType: cloudfront.FunctionEventType.VIEWER_REQUEST,
function: basicAuthCloudfrontFunction,
},
];
}
const remixDistribution = new cloudfront.Distribution(
this,
`remixDistribution`,
{
domainNames: [certificateDomain],
certificate,
defaultBehavior: {
allowedMethods: cloudfront.AllowedMethods.ALLOW_ALL,
cachePolicy,
origin: new origins.HttpOrigin(remixHttpApi?.url!.split('/')[2], {
customHeaders: { 'x-origin-verify': props?.xOriginVerify! },
}),
viewerProtocolPolicy:
cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.REDIRECT_TO_HTTPS,
functionAssociations: functionAssociations,
},
additionalBehaviors: {
[`/static/*`]: {
origin: new origins.S3Origin(staticBucket),
viewerProtocolPolicy:
cloudfront.ViewerProtocolPolicy.REDIRECT_TO_HTTPS,
functionAssociations: functionAssociations,
},
},
}
);
new route53.ARecord(this, 'SiteAliasRecord', {
recordName: siteDomain,
target: route53.RecordTarget.fromAlias(
new targets.CloudFrontTarget(remixDistribution)
),
zone,
});
}
}